PyTorch Basics to Advanced: A Complete Learning Guide 2026
What is PyTorch?
PyTorch is a powerful open-source deep learning framework used for building machine learning and artificial intelligence models. Moreover, it is written in Python and is designed to be intuitive, flexible, and easy to debug.
Unlike many traditional frameworks, PyTorch allows developers to build models dynamically. As a result, it feels more natural for Python developers and is widely used in research, education, and real-world AI applications.
Read More: Python Tutorial: A Simple and Beginner-Friendly Guide 2026
🔹 In simple words, PyTorch helps computers learn from data using neural networks. Moreover, this ability allows developers to build intelligent applications that can adapt and improve over time.
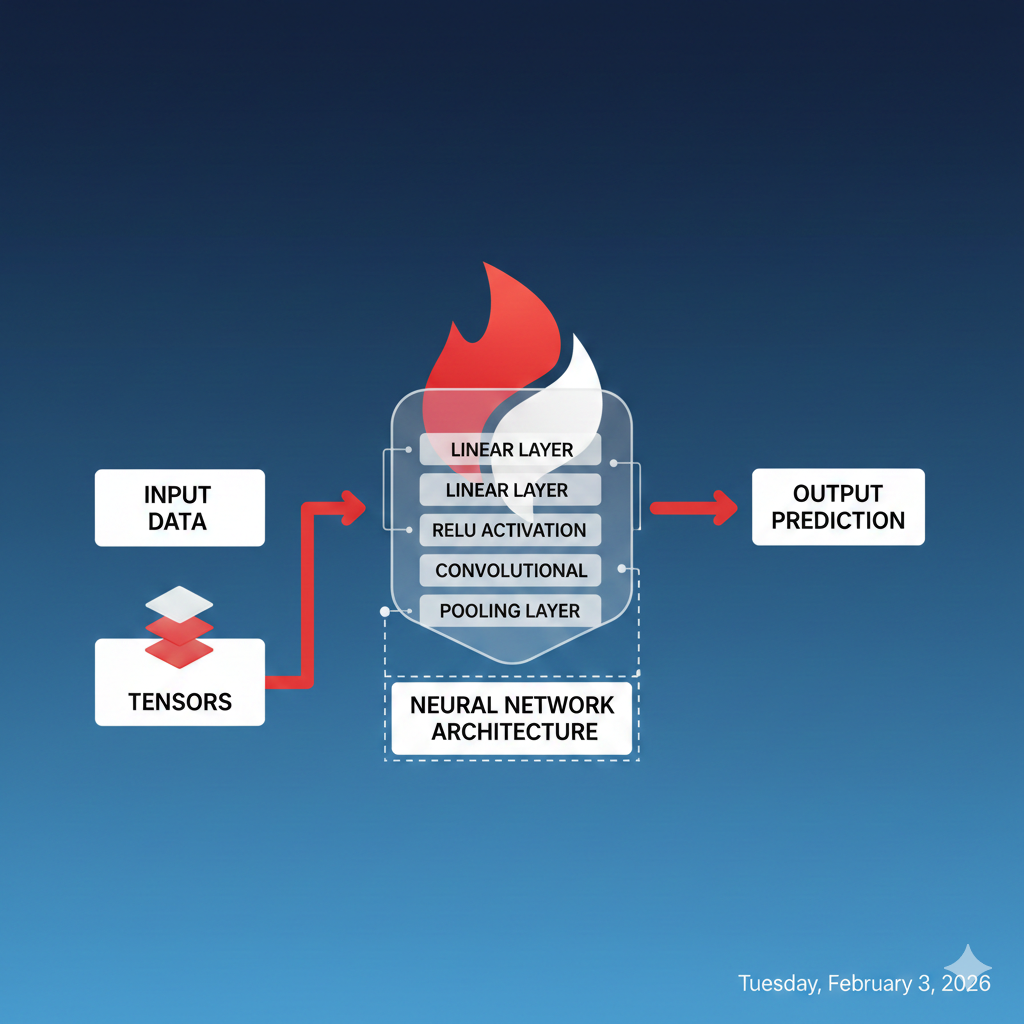
History of PyTorch
PyTorch was introduced in 2016 by Facebook AI Research (FAIR). In fact, it was built as a modern alternative to the older Torch framework, which, in contrast, was based on Lua.
Over time, PyTorch gained massive adoption because:
PyTorch simplified experimentation. Moreover, it supported dynamic graphs and, as a result, aligned well with Python’s ecosystem. Today, PyTorch is maintained by the PyTorch Foundation and, importantly, is supported by a global developer community. Furthermore, this strong support ensures continuous improvements, resources, and guidance for learners and developers worldwide. Moreover, this strong support ensures continuous updates, resources, and guidance for learners and developers worldwide.
Key Features of PyTorch
PyTorch stands out because of several strong features:
- Dynamic Computation Graphs – models change during runtime
- Easy Debugging – Pythonic and readable syntax
- GPU Acceleration – seamless CUDA support
- Autograd Engine – automatic gradient calculation
- Rich Ecosystem – torchvision, torchaudio, torchtext
Therefore, PyTorch is ideal for both beginners and advanced researchers.
PyTorch Neural Networks
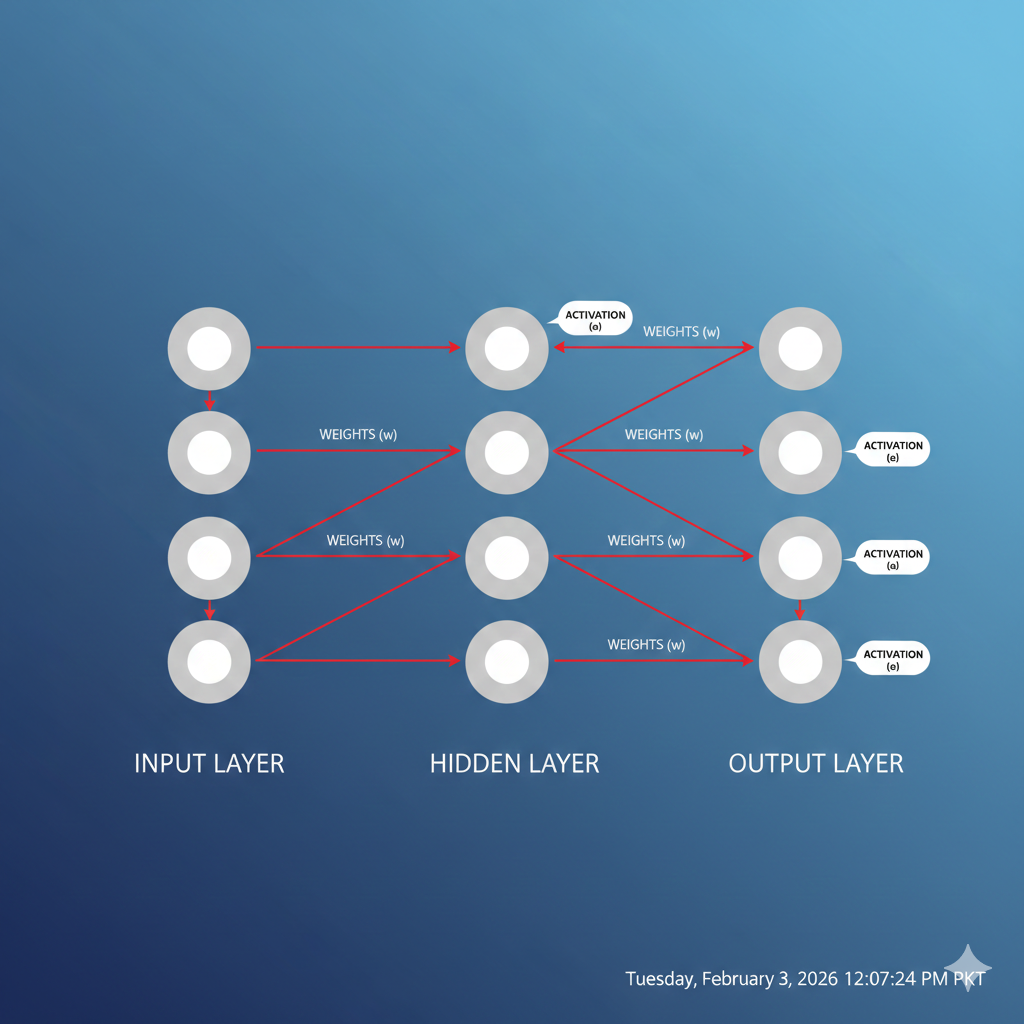
PyTorch provides the torch.nn module to build neural networks efficiently. Instead of manually coding every operation, developers can use prebuilt layers.
Common components include fully connected (Linear) layers, activation functions (ReLU, Sigmoid), and loss functions. Moreover, this modular approach makes neural network design faster and, consequently, cleaner.
Example: Simple PyTorch Neural Network
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SimpleNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleNN, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4, 8)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(8, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
return self.fc2(x)
model = SimpleNN()
print(model)
Output:
SimpleNN(
(fc1): Linear(in_features=4, out_features=8, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=8, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
🔍 This output shows the architecture of the neural network clearly.
PyTorch Tensors
Importantly, tensors are the backbone of PyTorch. They are multi-dimensional arrays similar to NumPy arrays but faster when used with GPUs.
import torch
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
print(x)
Tensors can store data, model parameters, and gradients efficiently.
Operations on Tensors
PyTorch supports a wide range of mathematical operations:
a = torch.tensor([2, 3])
b = torch.tensor([4, 5])
print(a + b)
print(a * b)
These operations are optimized for performance and scalability.

Reshaping and Transposing Tensors
Reshaping is essential when preparing data for neural networks.
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
reshaped = x.view(3, 2)
transposed = x.t()
print(reshaped)
print(transposed)
Output:
The tensor is reshaped into a new size, and additionally, its dimensions are swapped using transpose. 📌 As a result, this helps align data with model input requirements.
Auto grad and Computational Graphs:
Auto Grad and Computational Graphs:
It is, in fact, PyTorch’s automatic differentiation system. Moreover, it tracks operations and computes gradients automatically, making the training process much easier.
x = torch.tensor(4.0, requires_grad=True)
y = x ** 2
y.backward()
print(x.grad)
Output:
tensor(8.)
🔍 Autograd removes the need for manual calculus during training.
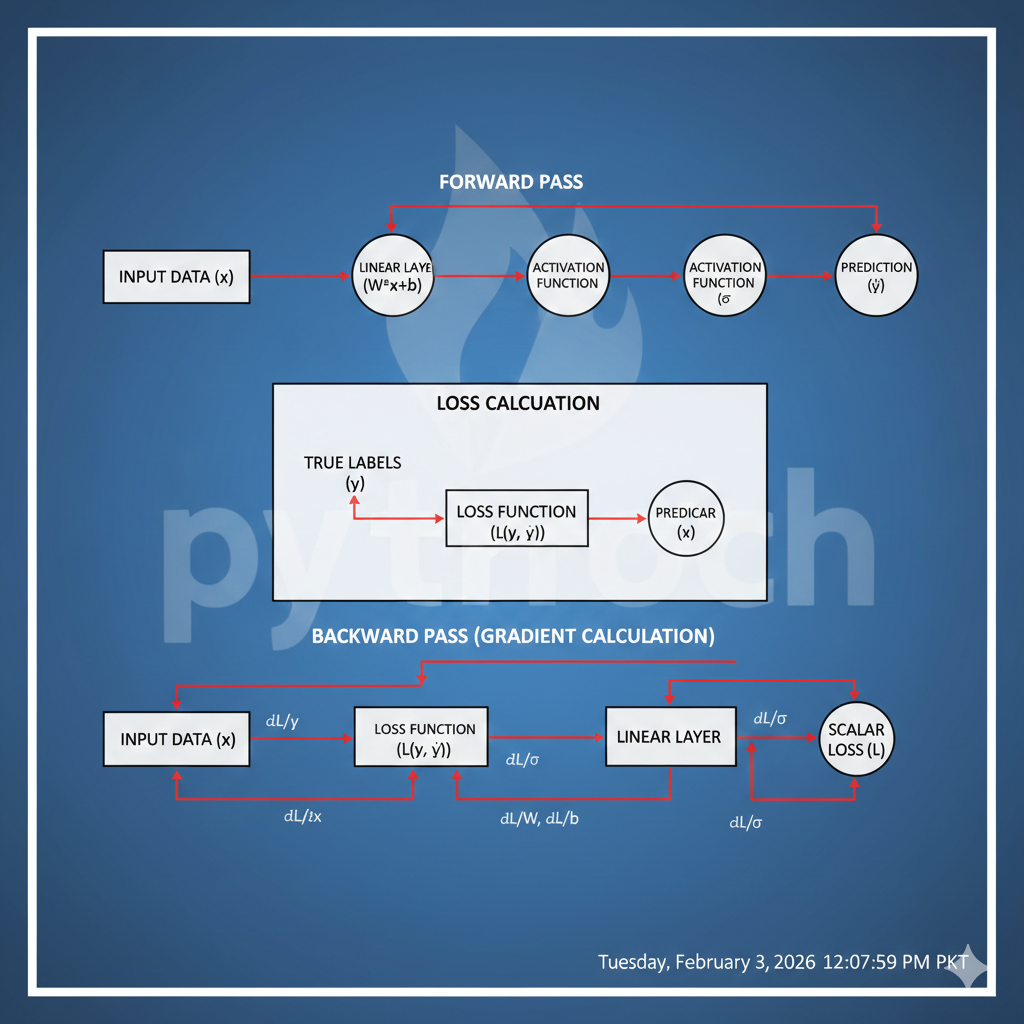
Building Neural Networks in PyTorch
Creating a neural network in PyTorch usually follows three steps:
- Define the model
- Choose loss function and optimizer
- Train the model
Moreover, this workflow keeps development organized and efficient.
Define Loss Function and Optimizer
Loss functions evaluate prediction errors, while optimizers update weights.
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
Adam optimizer is widely used because it adapts learning rates automatically.
Train the Model
for epoch in range(5):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(torch.randn(1, 4))
loss = loss_fn(outputs, torch.tensor([[1.0]]))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(loss.item())
Output:
0.82
0.61
0.45
0.32
0.20
📉 The decreasing loss shows that the model is learning effectively.
PyTorch vs TensorFlow
| Feature | PyTorch | TensorFlow |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Very Easy | Moderate |
| Graph Type | Dynamic | Static |
| Debugging | Simple | Complex |
| Research Use | Very High | Moderate |
| Production | Growing | Very Strong |
In contrast, PyTorch is preferred for research, while TensorFlow dominates large-scale deployment.
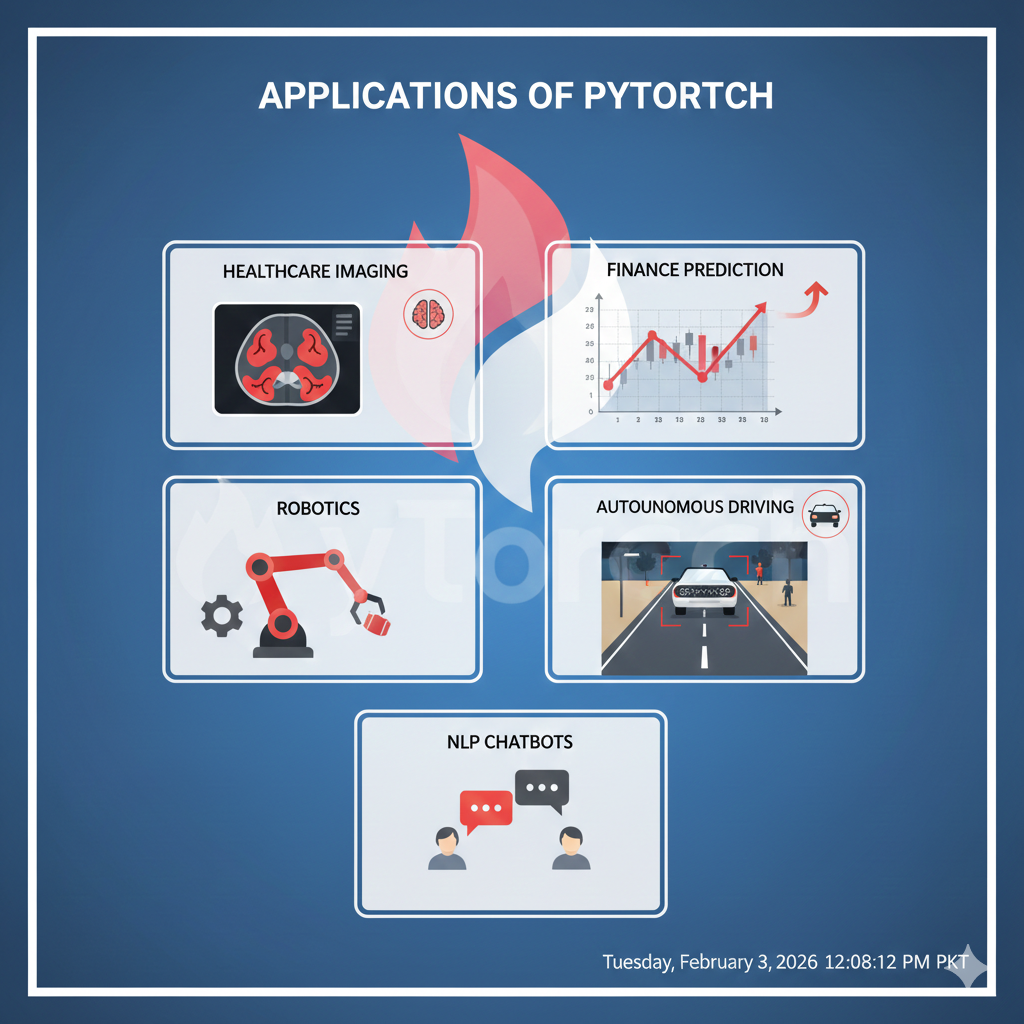
Applications of PyTorch
PyTorch is used in many real-world applications, including:
- Computer Vision
- Natural Language Processing
- Speech Recognition
- Autonomous Driving
- Medical Diagnostics
- Recommendation Systems
As a result, learning PyTorch opens doors to modern AI careers.
Read More: Text-to-Speech:A simple and Complete AI Voice Guide for 2026
Conclusion
PyTorch is, in fact, one of the most flexible and powerful deep learning frameworks available today. Moreover, its dynamic nature, strong community, and ease of use make it an excellent choice for anyone entering the world of artificial intelligence.
PyTorch FAQs (25)
1. What is PyTorch mainly used for?
PyTorch is mainly used for building and training deep learning and neural network models, especially in research and real-world AI applications.
2. Is PyTorch suitable for beginners?
Yes, PyTorch is beginner-friendly because its syntax is simple and closely follows standard Python programming.
3. Who developed PyTorch?
PyTorch was developed by Facebook AI Research (FAIR) and later supported by the PyTorch Foundation.
4. Is PyTorch free to use?
Yes, PyTorch is completely open-source and free, which means that, as a result, it is easily accessible for students, researchers, and companies alike. Moreover, this openness encourages community collaboration and innovation.
5. What programming language does PyTorch use?
PyTorch is primarily based on Python, although it also has a C++ backend for performance.
6. How is PyTorch different from NumPy?
Although PyTorch tensors are similar to NumPy arrays, PyTorch supports GPU acceleration and automatic differentiation.
7. What are PyTorch tensors?
PyTorch tensors are multi-dimensional data structures used to store data, model parameters, and gradients efficiently. Moreover, they enable fast mathematical operations on both CPUs and GPUs, which significantly accelerates model training.
8. Can PyTorch run on GPU?
Yes, PyTorch supports CUDA, which allows models to run faster on GPUs. Moreover, this capability significantly improves training speed for large-scale deep learning projects.
9. What is Autograd in PyTorch?
Autograd is PyTorch’s automatic differentiation engine that calculates gradients during backpropagation.
10. Why are dynamic computational graphs important?
Dynamic graphs allow developers to modify models during runtime, therefore making experimentation easier and faster.
11. Is PyTorch good for research?
Yes, PyTorch is extremely popular in research because it is flexible, readable, and easy to debug.
12. Can PyTorch be used in production?
Yes, however, PyTorch was initially research-focused, it is now widely used in production systems as well.
13. What industries use PyTorch?
PyTorch is used in healthcare, finance, robotics, autonomous driving, and natural language processing. Moreover, its versatility and flexibility make it suitable for a wide range of AI and machine learning applications across different industries.
14. What is torch.nn in PyTorch?
torch.nn is a module that provides building blocks such as layers, loss functions, and activation functions for neural networks.
15. How does PyTorch handle backpropagation?
PyTorch automatically handles backpropagation using Autograd, as a result reducing manual mathematical effort.
16. Is PyTorch faster than TensorFlow?
In contrast, speed depends on the use case; however, PyTorch is often faster during development and experimentation.
17. Which is better: PyTorch or TensorFlow?
Both are powerful; however, PyTorch is preferred for research, while TensorFlow is commonly used for large-scale deployment.
18. Can PyTorch be used for machine learning only?
No, PyTorch is mainly used for deep learning, but it can also handle traditional machine learning tasks.
19. What is a loss function in PyTorch?
A loss function measures how far a model’s predictions are from the actual values. Moreover, it plays a crucial role in guiding the optimizer to improve the model during training. Moreover, it helps guide the optimizer to improve the model during training, making learning more accurate and efficient.
20. What optimizers does PyTorch support?
PyTorch supports optimizers like SGD, Adam, RMSprop, and many others. In addition, choosing the right optimizer can significantly impact the speed and accuracy of model training.
21. Is PyTorch good for computer vision?
Yes, PyTorch is widely used in computer vision, especially with libraries like torchvision.
Read More: Computer Vision in AI: A Complete Beginner-Friendly Guide
22. Can PyTorch handle large datasets?
Yes, PyTorch provides data loaders and batching tools, which, as a result, allow it to efficiently manage large datasets. Moreover, these tools make training on big data much easier and faster for developers.
23. What is the role of epochs in PyTorch training?
Epochs represent the number of times the model processes the entire training dataset. In addition, increasing the number of epochs can improve the model’s learning, although too many epochs may lead to overfitting.
24. Does PyTorch have a strong community?
Yes, PyTorch has a large global community. Furthermore, it offers extensive documentation and active developer support, which helps learners and professionals resolve issues quickly and effectively.
25. Is learning PyTorch worth it in 2026?
Absolutely. As a result of growing AI adoption, PyTorch remains one of the most in-demand skills in machine learning and deep learning.
Read More: Principal Component Analysis: Learn It the Easy Way
🚀 Ready to Start Your PyTorch Journey?
If you want to learn PyTorch step by step, build real-world AI models, or need expert guidance for machine learning and deep learning, then now is, in fact, the perfect time to take action. Moreover, starting today can help you gain a competitive advantage in the AI field.
Whether you’re a beginner, a student, or a working professional, personalized support can help you move faster and avoid common mistakes.
📩 Get in Touch Today
- Email: zarirahc@gmail.com
- WhatsApp: +92 0311 0115488
- Website: https://minsaai.com/
- Don’t just read build, practice, and grow with expert support.














Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.