Decision Trees: A Complete Guide with Examples & Best Steps
Decision trees are one of the most widely used tools in data science, machine learning, and business analytics. They help turn complex data into simple, actionable decisions. Whether you are a student learning AI, a business analyst, or a data scientist, decision trees are essential for making accurate predictions and decisions. In this guide, you will learn:
What decision trees are?
How they work?
Types and terminologies
How is entropy used?
Splitting criteria
Pros and cons
Best practices
How to create decision trees?
How to use Confluence for effective decision tree documentation?
What is Decision Tree?
A decision tree is a supervised learning model that maps observations about data to conclusions or outcomes. It is called a “tree” because the structure resembles a tree with branches and nodes.
Key Points:
- Used for classification and regression
- Works by asking a series of questions
- Each question leads to a branch and final decision
- Helps in both data-driven decision making and predictive analysis
Example:
Imagine you want to predict whether a student will pass an exam based on:
- study hours
- sleep hours
- class attendance
A decision tree will ask questions like:
- “Did the student study more than 5 hours?”
- “Did the student attend more than 80% classes?”
Each answer leads to the final prediction: Pass or Fail.
Read More: What’s New in the AI Ecosystem? 2026 Trends You Must Know
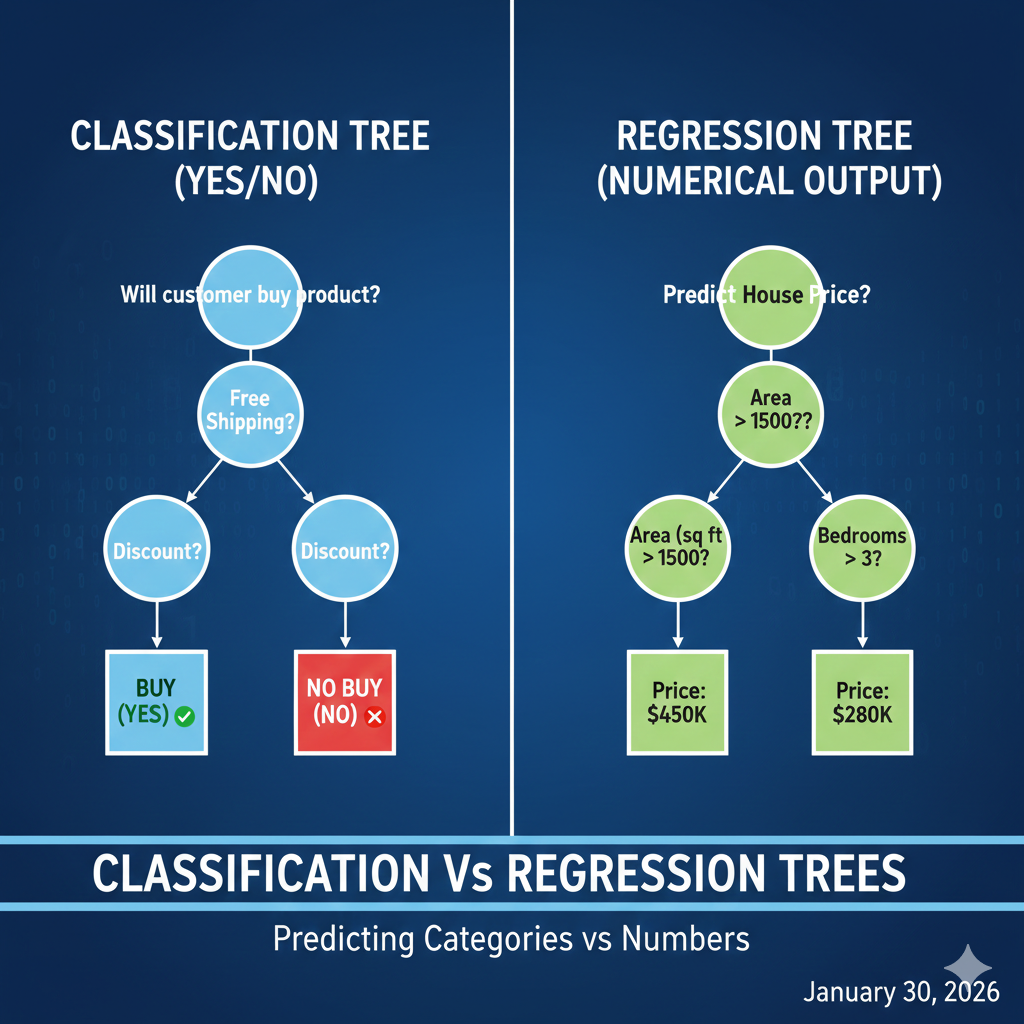
Types of Decision Trees
Decision trees are divided into two main types:
1. Classification Tree
Used when the target variable is categorical (e.g., yes/no, pass/fail).
Example:
Predicting if a customer will buy a product.
2. Regression Tree
Used when the target variable is continuous (e.g., price, salary).
Example:
Predicting house prices or sales revenue.
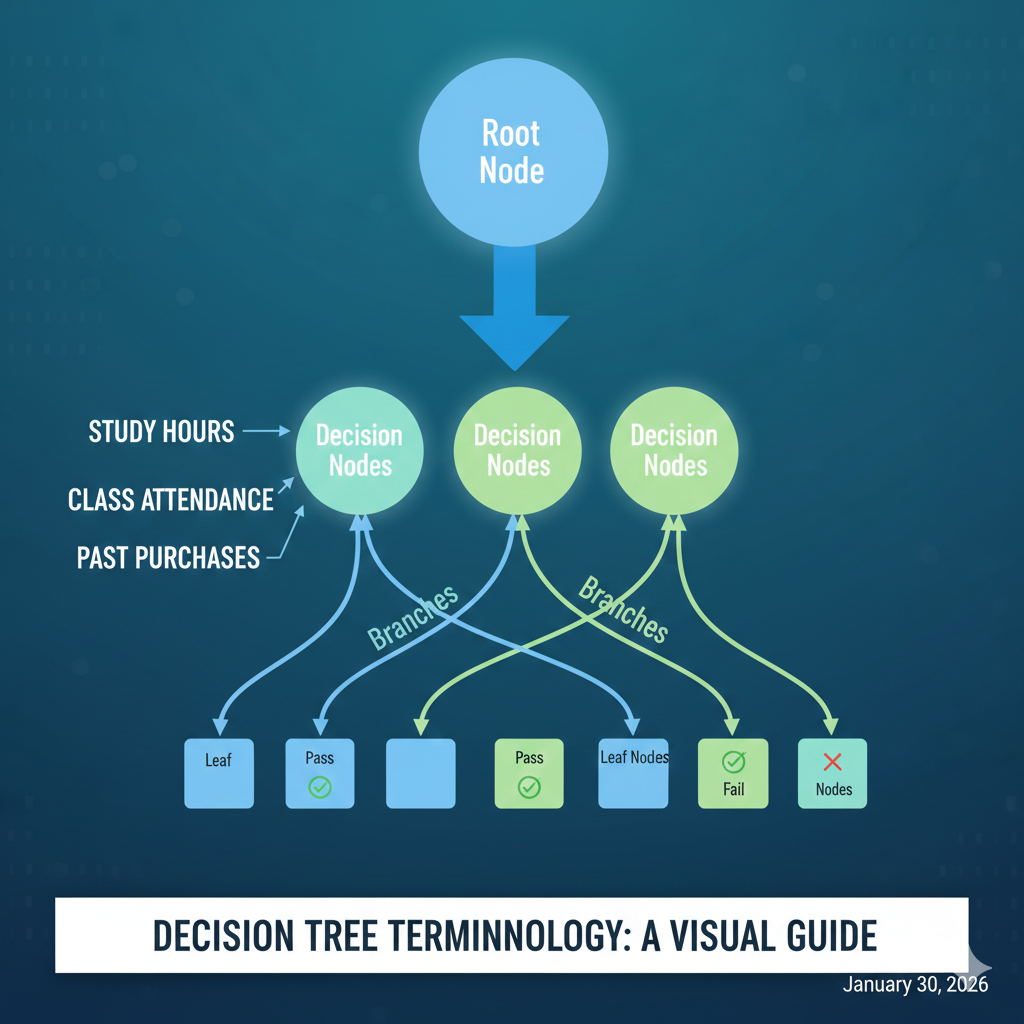
Decision Tree Terminologies
Before building a decision tree, you should understand these terms:
Root Node
The starting point of the tree where the first decision is made.
Decision Node
Nodes that split into further branches based on a feature.
Leaf Node
Final output node that represents the result or class label.
Branch
A path between nodes representing decision outcomes.
Parent Node
A node that splits into multiple child nodes.
Child Node
Nodes created after splitting a parent node.
How do Decision Trees use Entropy?
Entropy is a key concept in decision tree. It measures the amount of uncertainty or impurity in the dataset.
Entropy Formula:
Entropy = - Σ (p(i) * log2 p(i))
Where:
- p(i) is the probability of class i
- Σ is the sum of all classes
How It Works:
- If the data is pure (all belong to one class), entropy is low
- If the data is mixed, entropy is high
The decision tree algorithm chooses the feature that reduces entropy the most, making the dataset more organized
How Decision Trees Work?
Decision tree work through a process called recursive partitioning. Here is the step-by-step process:
Step-by-Step Working
- Start at the root node
- Select the best feature to split
- Split the data into subsets
- Repeat the process for each subset
- Stop when the data is pure or meets stopping criteria
Example:
Let’s predict whether a person will buy a product based on:
- Age
- Income
- Past purchases
The tree will keep splitting data until it reaches a decision.
Read More: What Are AI Ethical Frameworks? A Complete Responsible AI Guide

Splitting Criteria in Decision Trees
The splitting criteria determine how the tree splits data at each node. The most common splitting criteria are:
1. Information Gain
Measures how much information a feature provides about the class.
2. Gini Index
Measures impurity. Lower Gini means higher purity.
3. Chi-Square
Used to test the statistical significance of splits.
4. Gain Ratio
Improves Information Gain by reducing bias toward multi-valued attributes.
Decision Trees vs Random Forest vs Gradient Boosting
Many people confuse decision tree with other tree-based models. Here’s a simple comparison:
| Model | Best for | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Tree | Simple predictions | Easy to interpret | Overfitting risk |
| Random Forest | Better accuracy | Handles overfitting | Less interpretable |
| Gradient Boosting | High performance | Best for complex tasks | Slow training |
Read More: AI and Random Forest: The Ultimate Beginner-to-Pro Guide (2026)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Decision Trees
Advantages
- Easy to understand and interpret
- Can handle both numerical and categorical data
- No need for data normalization
- Fast and efficient
- Can help in feature selection
Disadvantages
- Prone to overfitting
- Sensitive to small changes in data
- Can become complex with large datasets
- May not be accurate for continuous variables without pruning
How to Create a Decision Tree
You can create decision trees using Scikit-Learn (Python).
Example Code:
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Load data
X = data.drop('target', axis=1)
y = data['target']
# Split data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
# Create model
model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
# Train model
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
# Accuracy
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, predictions))
Best Practices for Using Decision Trees

To create accurate and reliable decision trees, follow these best practices:
1. Avoid Overfitting
Use pruning and limit tree depth.
2. Use Cross-Validation
Check the model performance on different datasets.
3. Handle Missing Data
Use imputation to fill missing values.
4. Feature Engineering
Create meaningful features to improve accuracy.
5. Use Ensemble Methods
For better performance, use Random Forest or Gradient Boosting.
Read More: Supervised Learning in 2026: Best Methods, Models, and Uses
Create Effective Decision Trees with Confluence
Confluence is a powerful platform for documentation and collaboration. You can use Confluence to build and share decision trees.
How to Create Decision Trees in Confluence:
- Use draw.io integration
- Create clear nodes and branches
- Add explanations and notes for each decision
- Share with your team for feedback
- Update the tree in real time
Benefits:
- Centralized documentation
- Easy collaboration
- Clear visualization
- Version control
Conclusion
Decision tree is a powerful tool for making data-driven decisions. They are easy to understand and can handle complex datasets. By using entropy, splitting criteria, and best practices, you can build accurate decision trees that deliver real value.

Call to Action
If you found this guide helpful, feel free to reach out for personalized help or consulting.
📧 Email me at: zarirahc@gmail.com
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a decision tree, and why is it useful?
A decision tree is a predictive model that helps in decision-making, and it is useful because it simplifies complex data into easy-to-follow steps.
2. How does a decision tree work in machine learning?
First, it selects the best feature to split the data, then it repeats the process recursively, and finally it reaches a conclusion at the leaf nodes.
3. What is the difference between classification and regression trees?
Classification trees predict categories, whereas regression trees predict continuous values, such as price or revenue.
4. What is entropy, and how is it used in a decision tree?
Entropy measures data uncertainty, and decision trees use it to determine the best feature that reduces uncertainty after splitting.
5. What is information gain in decision trees?
Information gain calculates how much entropy decreases after a split, and it helps choose the most informative feature.
6. How is Gini Index different from entropy?
Gini Index measures impurity similarly, but it is often faster and simpler, and it is commonly used in decision tree algorithms.
7. What is pruning, and why is it important?
Pruning reduces tree size, and it is important because it prevents overfitting and improves model performance.
8. How can decision trees handle missing values?
A decision tree can handle missing values by using imputation and also by using specific algorithms that support missing data.
9. Why do decision trees overfit, and how can you prevent it?
Decision tree overfit because they become too complex, but you can prevent it by limiting depth and using pruning techniques.
10. What are the advantages of using decision trees?
These trees are easy to interpret, and moreover, they can handle both numerical and categorical data without scaling.
11. What are the limitations of decision trees?
They are sensitive to data changes, and therefore small changes can lead to different tree structures.
12. How do decision trees compare to random forests?
Random forests use multiple decision trees, and as a result they provide better accuracy and stability.
13. When should you use a decision tree instead of other models?
You should use a decision tree when interpretability is important, and when you need quick insights from data.
14. Can decision tree be used for both classification and regression?
Yes, decision tree can be used for both, and they are versatile tools for different types of predictions.
15. How do you choose the best splitting criteria?
You choose based on the dataset, and commonly use entropy, Gini, or gain ratio depending on the task.
16. What is gain ratio, and why is it used?
Gain ratio adjusts information gain by considering the number of split values, and thus it reduces bias toward features with many values.
17. How do decision trees handle categorical data?
Decision tree can directly split categorical data, and they work well without requiring encoding in many cases.
18. What is cross-validation, and why is it needed?
Cross-validation tests model performance on multiple datasets, and therefore it ensures that the model generalizes well.
19. How do you build a decision tree using Python?
You can use scikit-learn, and the process includes splitting data, training the model, and evaluating accuracy.
20. How can Confluence help in creating decision trees?
Confluence allows teams to document and visualize a decision trees, and moreover, it supports collaboration and real-time updates.
1. What is a decision tree, and why is it useful?
A decision tree is a predictive model that helps in decision-making, and it is useful because it simplifies complex data into easy-to-follow steps.
2. How does a decision tree work in machine learning?
First, it selects the best feature to split the data, then it repeats the process recursively, and finally it reaches a conclusion at the leaf nodes.
3. What is the difference between classification and regression trees?
Classification trees predict categories, whereas regression trees predict continuous values, such as price or revenue.
4. What is entropy, and how is it used in decision trees?
Entropy measures data uncertainty, and decision trees use it to determine the best feature that reduces uncertainty after splitting.
5. What is information gain in decision trees?
Information gain calculates how much entropy decreases after a split, and it helps choose the most informative feature.
6. How is Gini Index different from entropy?
Gini Index measures impurity similarly, but it is often faster and simpler, and it is commonly used in decision tree algorithms.
7. What is pruning, and why is it important?
Pruning reduces tree size, and it is important because it prevents overfitting and improves model performance.
8. How can decision trees handle missing values?
Decision trees can handle missing values by using imputation, and also by using specific algorithms that support missing data.
9. Why do decision trees overfit, and how can you prevent it?
Decision trees overfit because they become too complex, but you can prevent it by limiting depth and using pruning techniques.
10. What are the advantages of using decision trees?
Decision trees are easy to interpret, and moreover they can handle both numerical and categorical data without scaling.
11. What are the limitations of decision trees?
They are sensitive to data changes, and therefore small changes can lead to different tree structures.
12. How do decision trees compare to random forests?
Random forests use multiple decision trees, and as a result they provide better accuracy and stability.
13. When should you use a decision tree instead of other models?
You should use decision trees when interpretability is important, and when you need quick insights from data.
14. Can decision trees be used for both classification and regression?
Yes, decision trees can be used for both, and they are versatile tools for different types of predictions.
15. How do you choose the best splitting criteria?
You choose based on the dataset, and commonly use entropy, Gini, or gain ratio depending on the task.
16. What is gain ratio, and why is it used?
Gain ratio adjusts information gain by considering the number of split values, and thus it reduces bias toward features with many values.
17. How do decision trees handle categorical data?
Decision trees can directly split categorical data, and they work well without requiring encoding in many cases.
18. What is cross-validation, and why is it needed?
Cross-validation tests model performance on multiple datasets, and therefore it ensures that the model generalizes well.
19. How do you build a decision tree using Python?
You can use scikit-learn, and the process includes splitting data, training the model, and evaluating accuracy.
20. How can Confluence help in creating decision trees?
Confluence allows teams to document and visualize decision trees, and moreover it supports collaboration and real-time updates.
Call to Action
If you found this guide helpful, feel free to reach out for personalized help or consulting.
📧 Email me at: zarirahc@gmail.com














Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.