AI and Random Forest: The Ultimate Beginner-to-Pro Guide (2026)
Introduction
Random Forest in AI is one of the most reliable algorithms in Artificial Intelligence and, as a result, is widely used for building accurate and stable machine learning models. By contrast to relying on a single model, Random Forest combines multiple decision trees; consequently, it improves prediction accuracy, reduces overfitting, and performs exceptionally well on complex and noisy datasets. Moreover, from spam detection and medical diagnosis to fraud prevention and recommendation systems, this algorithm plays a crucial role in real-world AI applications, thereby making it an essential concept for anyone learning or working in AI and machine learning.
What Is Random Forest in AI?
Random Forest is a powerful machine learning algorithm used in AI to make accurate predictions and decisions. Instead of relying on a single model, it builds multiple decision trees and combines their results to produce a final output. This approach enhances reliability, stability, and accuracy, especially when dealing with large, complex, or noisy datasets.
Why It Is Important in AI
Many AI models fail because of overfitting, where they perform well on training data but poorly on new data. Random Forest solves this problem by:
- “Instead of using just one tree, it is often more effective to use multiple trees. By doing so, not only can we increase stability, but we can also improve overall performance. Furthermore, combining the strengths of several trees can help mitigate the weaknesses of any single tree.”
- Training each tree on different data samples
- Combining predictions through majority voting or averaging
Random Forest is important in AI because it effectively balances accuracy and reliability; moreover, it minimizes overfitting by combining multiple decision trees instead of relying on a single model. As a result, it performs consistently well on complex and noisy datasets. In addition, Random Forest handles missing data and feature interactions efficiently; therefore, it is widely adopted in real-world applications. Overall, due to its robustness and versatility, Random Forest remains a crucial algorithm in Artificial Intelligence.
This makes Random Forest one of the most trusted algorithms in AI and machine learning.
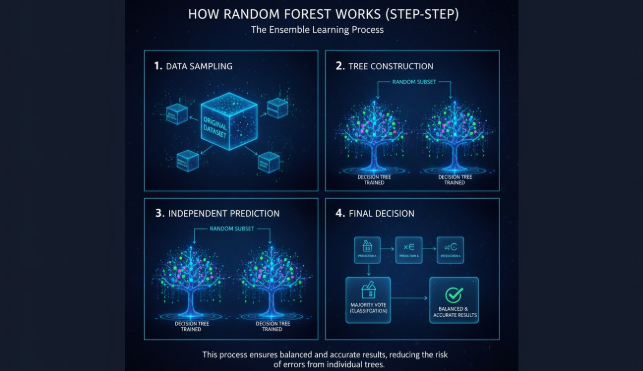
How It Works (Step-by-Step)
1. Data Sampling
Random subsets of data are created from the original dataset.
2. Tree Construction
A decision tree is trained on each subset.
3. Independent Predictions
Each tree makes its own prediction independently.
4. Final Decision
- Classification: Majority vote among trees
- Regression: Average of all tree predictions
This process ensures balanced and accurate results, reducing the risk of errors from individual trees.
Real-World Applications of Random Forest in AI
Random Forest in AI is widely used in practical AI applications such as:
- Spam email detection
- Medical diagnosis systems
- Credit risk analysis
- Fraud detection
- Customer churn prediction
- Recommendation systems
Because it handles large datasets and complex data well, Random Forest is ideal for data-driven AI solutions.
Random Forest in AI for Classification and Regression
- Classification: Used for categorical outputs (e.g., spam vs. not spam, disease vs. no disease)
- Regression: Used for numerical outputs (e.g., sales forecasting, price prediction)
This versatility makes Random Forest a core algorithm for AI projects.
Random Forest in AI vs Decision Tree
| Feature | Random Forest | Decision Tree |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High | Moderate |
| Overfitting | Low | High |
| Stability | Strong | Weak |
| Complexity | Higher | Simple |
In AI systems, Random Forest is preferred when accuracy and reliability matter.
Advantages of Random Forest in AI
- High prediction accuracy
- Reduces overfitting
- Works well with large datasets
- Handles missing data effectively
- Suitable for both classification and regression
Limitations of Random Forest in AI
- Slower than simple models
- Less interpretable than decision trees
- Requires more computational power
Despite these limitations, Random Forest remains a top choice in AI development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Random Forest in Artificial Intelligence
Random Forest is a machine learning algorithm that combines multiple decision trees to produce accurate predictions for classification and regression.
Importance of Random Forest in AI
It reduces overfitting, handles complex datasets, and delivers higher accuracy compared to a single decision tree.
Accuracy Improvement in Random Forest
Random Forest improves accuracy by training multiple decision trees on different data samples and combining their predictions through voting or averaging.

Learning Type of Random Forest
Random Forest is a supervised learning algorithm that requires labeled data for training.
Use of Random Forest for Classification and Regression
It can handle categorical outputs for classification and numerical outputs for regression tasks.
Problems Best Solved by Random Forest
Random Forest works best with large datasets, noisy or missing data, and complex decision boundaries.
Difference Between Random Forest and Decision Tree
Random Forest uses multiple trees to improve accuracy and reduce overfitting, whereas a decision tree relies on a single tree.

Feature Scaling Requirement in Random Forest
Random Forest does not require feature scaling.
Suitability of Random Forest for Beginners
Random Forest is beginner-friendly because it is easy to implement and requires minimal parameter tuning.
Advantages of Random Forest in AI
Key advantages include high accuracy, reduced overfitting, robust performance, effective handling of missing data, and versatility in classification and regression.
Disadvantages of Random Forest
Its limitations include slower computation, reduced interpretability, and higher resource consumption.
Comparison Between Random Forest and Deep Learning
Random Forest often outperforms deep learning on small to medium datasets; however, deep learning is more effective for large-scale, unstructured data.
Handling Missing Values in Random Forest
Random Forest can manage missing values efficiently without extensive preprocessing.
Real-World Applications of Random Forest
It is widely used in fraud detection, medical diagnosis, recommendation systems, and other real-world AI applications.
Overfitting Behavior of Random Forest
As a result, Random Forest significantly reduces overfitting by averaging the predictions of multiple decision trees.
Optimal Number of Trees in Random Forest
Typically, using 100–500 trees provides strong performance, depending on dataset size and complexity.
Use of Random Forest in Production AI Systems
It is commonly deployed in production due to its stability and reliable predictive performance.

Random Forest and Overfitting Behavior
Random Forest significantly reduces overfitting by averaging the predictions of multiple decision trees. As a result, it improves generalization and produces more stable outcomes compared to individual trees.
Optimal Number of Trees in a Random Forest
Typically, using 100–500 trees delivers strong performance. However, the ideal number may vary depending on the dataset’s size, complexity, and available computational resources.
Ready to Build Smarter AI Solutions with Random Forest?
If you want to learn AI concepts deeply, apply Random Forest in real projects, or need expert guidance for AI and machine learning, now is the perfect time to take action.
We help beginners, bloggers, and tech learners understand Random Forest in AI in a simple, practical, and results-driven way.
📞 Contact Us Today
Email: zarirahc@gmail.com
Website: minsaai.com
✅ Why Connect With Us?
- Beginner-friendly AI explanations
- Practical Random Forest guidance
- SEO & AEO-optimized AI content
- Fast response & expert support
Start your AI journey today and turn knowledge into real-world impact.













Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.